Explanation of Computer Networks
A network is a set of devices or nodes that are connected via communication media or channel. A printer, computer any machine that is capable of communication on network is referred to as a device or node.
Need of Computer Networks
Sharing the resources such as printer array all the users, Sharing of expensive softeners and database, Communication from one computer to the other, Exchange of data and information among st the users, via the network, Sharing of information over geographically wide areas, For connecting the computers between various building of an organization.
Components of Computer Network
Hardware Component
Serves: Serves are High-Configuration Computer that manage the resources of the network. The network operating system is typically installed in the server.
Clients:- Clients are computers that requested to the sever and receive services from the network to access and use the network resources.
Peers:- Peers are computer that provide as well as receive services from other peers in work group network resources.
Transmission media:- Transmission media are the channel through which data is transferred from one device to another in a network.
Connecting Devices: Connecting devices act as middle ware between networks or computers by binding the network media together. Some of the common connecting are:
Routers, Bridges, Hubs, Repeaters, Gateways, Switches
Software Components
Networking Operating System: Network Operating System is typically installed in the server and facilitates workstations in a network to share files, database, applications, printers etc.
Protocol suite:- A protocol is a rule or guideline followed by each computer for data communication protocol suite is a set of related protocol that are laid down for computer networks. The two popular protocol suites are:-
A) ASI Model (open source interconnections)
B) TCP/IP Model
Open system Interconnection (OSI) Model
It is the foundation for all communication that takes place between computers and other networking devices.
There are seven layers in OSI reference model.
Physical Layer, Data link layer, Network layer, Transport Layer, Session layer, Presentation layer, Application layer
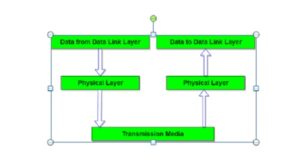
Layer 1: Physical layer
It is responsible for the actual physical connection between the devices; such physical may be made by using twisted pair, fiber optic, and communication media. Physical layer is concerned with transmitting row bits over a communication channel.
It deals with Mechanical and Electrical Specification of interface and transmission medium and also defines the procedures and functions that physical devices and interfaces have to perform for data transmission.
Function of physical layer
Transforming it into signals: The data at physical layer consist of sequence of bits. The physical layer transforms these bits into signals by using different encoding schemes so that data can be transmitted across the physical medium.
Bit Synchronous: The physical layer provides the synchronous of the bits by provide a clock.
Provides Physical Characteristics of Interfaces and medium
Physical layer manages the way a device connects to the network media.
Bit rate control: Physical layer defines the transmission rate i.e. the number of bits sent in one second.
1. Line configuration:-
Physical layer also defines the way in which the devices are connected to the medium.
2. Transmission mode:-
Physical layer also defines the way in which the different devices nodes are arranged.
3. Multiplexing:-
Physical layer can use different techniques of multiplexing in order to improve the channel efficiency.
4. Circuit switching:-
Physical layer also provides the circuit switching to interconnect different networks.
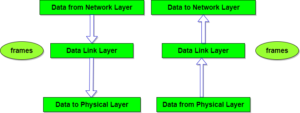
Layer 2: Data Link Layer
Data link layer is the second layer, layer 2, of OSI model.
1. It is responsible for reliable node to node delivery of data. It receives the data from network layer and creates frames, add Physical Address to these frames and pan them to physical layer.
DIAGRAM OF DATA LINK LAYER
Logical link layer: It provides interface between the media access methods and network layer protocol such as internet protocol which is part of TCP/IP Protocol Suite.
Medium access control: Is responsible for connection to physical media. At the MAC address is added to the pocket, such a packet is called a frame that contains all the addressing information necessary to travel from source device to destination device
Function of data link layer
Framing: Data link layer is responsible for dividing the stream of bits received from network layer into small data units called frames.
Physical addressing: After creating frames, data link layer adds physical address of sender end/ or receiver in the header of each frame.
Flow Control: It is the traffic regulatory mechanism implemented by data link layer that prevents the fast sender from dawning the slow receiver.
Error Control: Data link layer provides the mechanism of error control in which it detects and transmits damaged or lost frames.
Access control: When transmitting the frames, the system waits from the feedback.
Layer 3: Network layer
A network layer is the 3rd layer-3 of OSI model.
· It is responsible for the source to destination delivery of a packet across multiple networks.
· If two systems are attached to different network with connecting devices like routers b/w the network.
· Thus data link layer overseas, the delivery of the pocket between the two systems on same network layer link ensures that the packet gets from its point of point of origin to its final destination.
Functions of networks of network layer
Logical Addressing: Physical addressing provided by data link layer handles the addressing problem if the data are to be sent within the same network i.e. locally. Network layer provides another addressing system called logical addressing system called logical the deals with the transfer of data across the network.
Rating:When indecent networks are connected together to create inter networks served possible routes are available to send the data from source to destination.
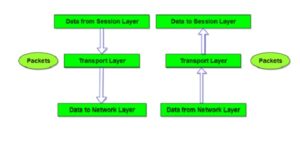
Layer 4: Transfer layer
Transport layer is the fourth of OSI model. It is responsible for source to destination delivery of entire manage.
· It also looks after error control & flow control at source-to-destination level.
· Application layer programs interact with each other using the services of transport layer.
· Therefore, Transport layer provides services to application layer & taken services from network layers.
· A connection is single logical path between the source and destination that is annunciation with all the packets in a manage.
Function of transport Layer
Segmentation of message into packet & reassembly of packets into manage:-
The basic function of transport layer is to accept the data from session layer and split it into smaller units called packets such that each unit contains a specific sequence number.
Connection management: As disused earlier transport layer provides two types of services:-
Connection oriented and connection len.
Service Point Addressing: The purpose of transport layer in to delivery manage for one person an source machine to another process running an destination machine.
Flow control: Link data link layer, transport layer also performs flow control. Transport layer makes sure that the sender and receiver communicate at a rate they both can handle.
Error control: Like data link layer, transport layer also performs error control. Here control is performed end to end rather than across a single link.
Layer 5: Session layer
Session layer is the fifth of OSI model. It is also provides for orderly communication between devices by regulating the flow of data. The responsibility and relationship of session layer with transport and presentation layer.
Function of session layer
Establishment maintaining and ending a session
When a sending devices first contacts a receiving device, it sends a syn (synchronization) packet establish communication and information will be sent.
Dialog control: Dialog control is the function of session layer that determines which device will communicate will transmit at a given time as well as controlling the amount of data that can be sent in a transmission.
Dialog Separation or Synchronization: The session layer is also responsible for adding checkpoint or markers within the manage. This process of inserting marks to the stream of data is known as dialog separation.
Layer 6: Presentation of layer
· It is concerned with the syntax and emanation of the information exchanged between the two devices.
· The relationship of presentation layer is shown in the below detailed point.
Functions of presentation layer
Data Presentation Layer: These functions ensure that the data being sent is in the format that the recipient can process.
Data encryption: Data encryption is a tool allows us to hide information from everyone except the person who originally sent the information and the intended recipient.
Data compression:Another important function of presentation of presentation layer is data compression layer shrinks large amount of data into smaller pieces i.e. it reduces the number of bits to be transmitted.
Layer 7: Application Layer
· It enables the users whether human or software, to access the network by providing user interfaces.
· It provides services that directly support user application on another computer as though they were on same computer.
· Protocol functioning at application large work with application you use to communicate over network.
Function of application layer
Network virtual terminal: A Network Virtual Terminal is a software version of a physical terminal and allows a user to log onto a remote host.
File Transfer access and management: This application allows a user to access fill in a remote host to make change or to read data to receive file.
Mail services:This application provides various e-mail services such as e-mail forwarding and storage.
Directory services: This application provides the Distributed Database Sources and access for global information about various objects and services.




Fast and easy to set up.